Manual filling processes can be time-consuming, imprecise, and labor-intensive, resulting in inconsistent product quality and inefficiency. Automatic filling machines offer a solution, delivering precise, high-speed filling processes across industries.
The Working Principle of Automatic Filling Machines
An automatic filling machine operates using advanced control systems, including sensors, actuators, and programmable logic controllers (PLCs). These components work together to detect containers, measure volumes accurately, and dispense products with minimal human intervention.

Key Steps in the Filling Process
Container Detection
Sensors identify the presence and positioning of containers on the production line. This ensures precise alignment for filling.
Activation of Filling Mechanisms
Once the container is detected, the PLC triggers actuators to dispense the pre-programmed volume of product into the container. This ensures accuracy and reduces waste.
Post-Fill Operations
The system may include sealing, capping, or further labeling, ensuring the product is ready for packaging or distribution.
Types of Automatic Filling Machines
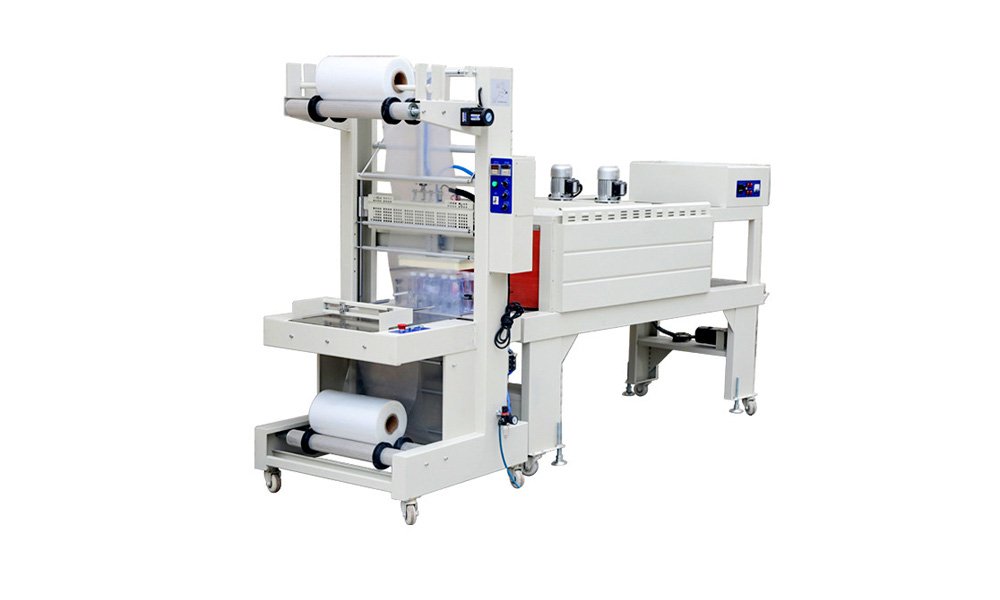
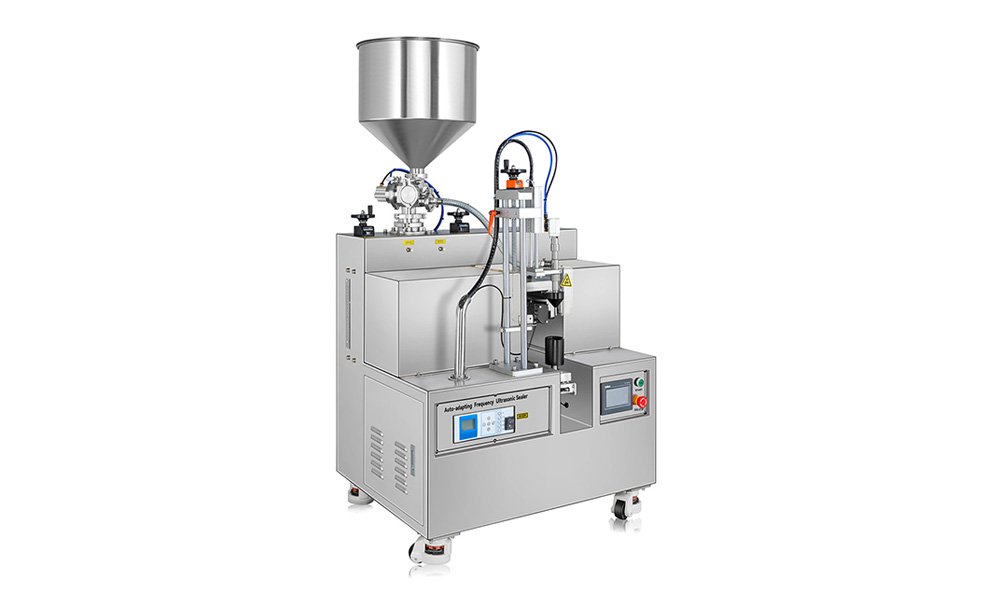
Liquid Filling Machines
Designed to handle various viscosities, from water to syrups. Technologies include gravity, pump, and vacuum fillers.
Capsule Filling Machines
Used in pharmaceutical industries for accurate powder or granule dispensing. They utilize tamping, auger, or vibratory filling methods.
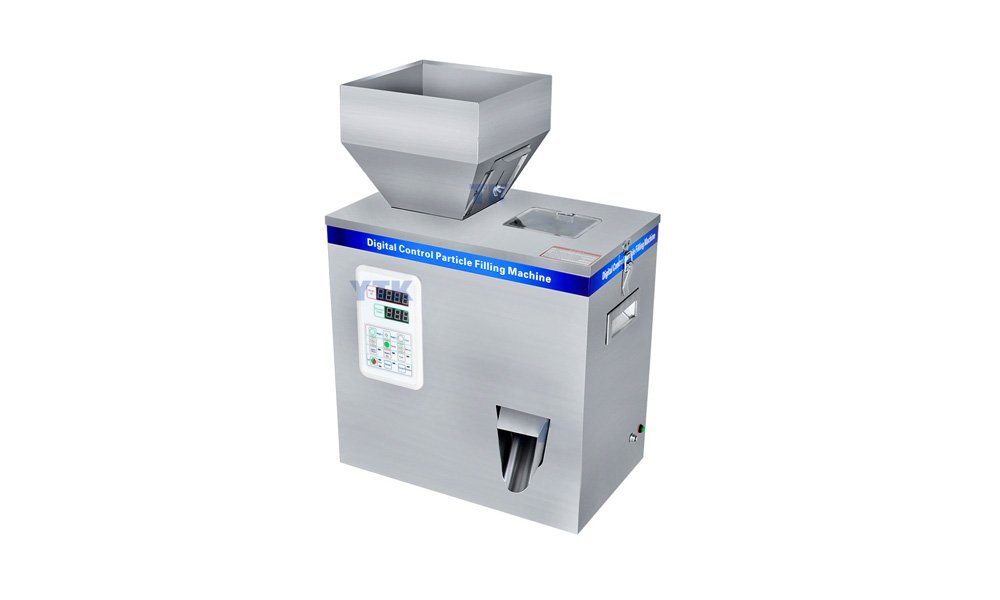
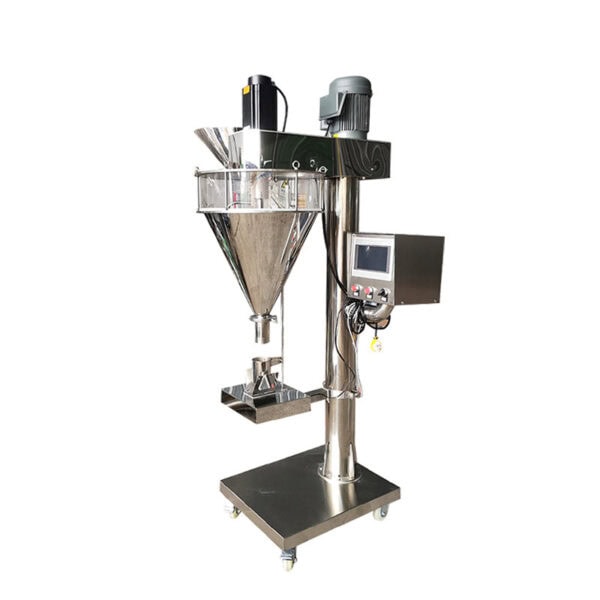
Powder Filling Machines
Ideal for dry substances, such as spices or chemicals, relying on augers or weigh-fill systems to achieve accuracy.
Advantages of Automatic Filling Machines
- Precision and Consistency: Ensures uniformity in fill volumes, reducing waste.
- Increased Efficiency: Handles high-volume production with ease.
- Enhanced Safety: Reduces manual handling of potentially hazardous substances.
Industry Applications
Automatic filling machines are crucial in industries such as:
- Food and Beverage: Bottling machines for liquids, including juices and sauces.
- Pharmaceuticals: Capsule filling machines for medicines and supplements.
- Cosmetics: Precise filling of creams, lotions, and serums.
Real-World Examples of Technology
- Bottle Filling Machines: Widely used for liquid products, equipped with adjustable settings for various bottle sizes.
- Label Printers: Often paired with filling machines to ensure proper identification and branding of packaged goods.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Common Issues
- Nozzle Clogging: Caused by viscous or particulate products.
- Sensor Malfunction: Leads to misaligned containers.
Preventative Measures
- Regular cleaning of machine components, including nozzles and sensors.
- Periodic calibration of PLCs to ensure accuracy and consistency.
Future Trends in Filling Machine Technology
- IoT Integration: Remote monitoring and predictive maintenance.
- AI Applications: Enhancing quality control through real-time analytics.
- Customizable Solutions: Modular designs for industry-specific needs.
Conclusion
Automatic filling machines revolutionize manufacturing, offering precision and efficiency in industries ranging from food to pharmaceuticals. Their evolving technology ensures they remain indispensable to modern production lines.