Businesses need reliable solutions for handling, storing, and displaying products in bulk. Without efficient secondary packaging, companies risk damage, increased costs, and waste. Secondary packaging machines provide critical protective, organizational, and branding benefits, ensuring products reach their destination safely and professionally.
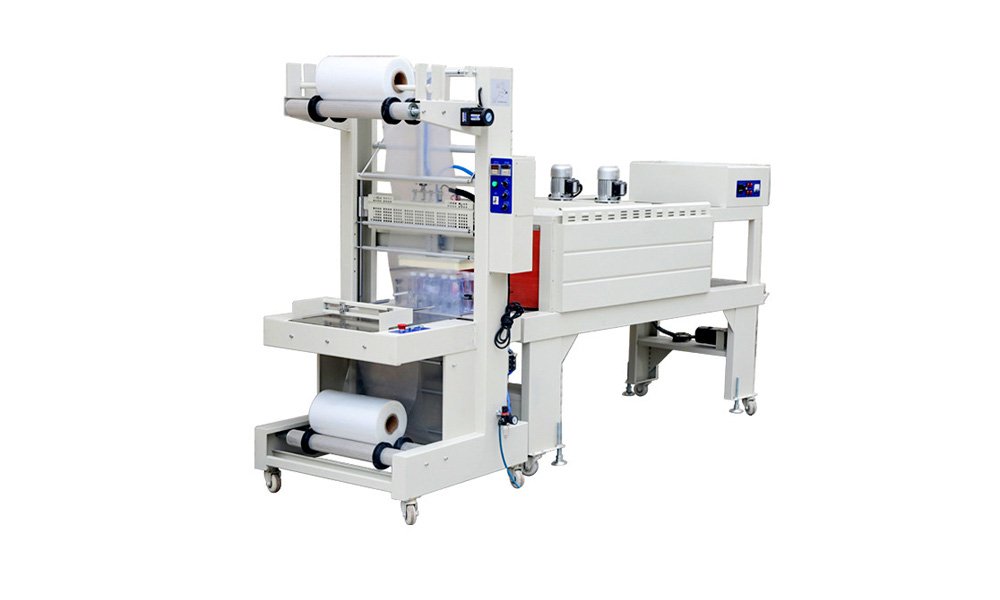
Secondary packaging machines are essential for grouping, protecting, and enhancing the appearance of products. Common types include carton formers, case packers, and shrink wrappers, which streamline handling and improve efficiency. These machines play a vital role in ensuring products reach consumers intact and with appeal.
Secondary packaging offers a vital layer of protection and marketing for various industries. Let’s delve into its role and the machines used in the process.

What is a Secondary Packaging Machine?
Secondary packaging machines bundle primary-packaged items for easier bulk handling, display, and transportation. Unlike primary packaging, which directly encases a product, secondary packaging surrounds multiple primary units.
A secondary packaging machine packages multiple primary units into larger bundles, using cases, cartons, or pallets to enhance protection, branding, and transportation.
These machines are widely used in industries like food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and electronics. By grouping items together, secondary packaging protects products and makes handling simpler. Whether it’s preparing products for display or ensuring safe transit, secondary packaging machines contribute to streamlined packaging and distribution.

What Types of Secondary Packaging Machines Are There?
Secondary packaging machines vary in type, each designed to meet specific requirements for packing, protecting, and organizing items in bulk. Key types include case packers, shrink wrappers, palletizers, and carton formers.
Examples of secondary packaging machines include case packers, shrink wrappers, palletizers, and carton formers, used for efficient packing and bulk handling.
- Case Packers: Stack and seal cases, providing structure and protection for products.
- Shrink Wrappers: Wrap items tightly for added security and moisture resistance.
- Palletizers: Arrange packed items on pallets for easier large-scale distribution.
- Different machines suit various production needs based on product size, weight, and transportation conditions.
What is the Role of Secondary Packaging in Pharmaceuticals?
In the pharmaceutical industry, secondary packaging is essential for safety, contamination prevention, and compliance with regulatory standards. By packaging products in durable, protective materials, it ensures that medicines remain safe during handling and transportation.
In pharmaceuticals, secondary packaging secures products, provides essential information, and ensures compliance with industry standards.
Secondary packaging in pharmaceuticals typically involves placing individually packaged units into larger boxes or cartons. This packaging helps prevent tampering and provides a surface for important information, such as dosage guidelines, lot numbers, and safety warnings. By meeting these industry requirements, secondary packaging machines help maintain product integrity and protect public health.
How Does Secondary Packaging Differ from Primary Packaging?
The main difference between primary and secondary packaging is their function: primary packaging encases individual products, while secondary packaging groups products for distribution and storage.
Primary packaging directly encases the product, whereas secondary packaging holds multiple units for storage, transport, and presentation.
- Primary Packaging: Encases the product itself (e.g., a pill bottle or liquid container).
- Secondary Packaging: Holds several primary packages together, typically using boxes or shrink wrap, for ease of transport and retail display.
For example, a labeling machine might apply branding and information labels to individual bottles (primary packaging), while secondary packaging could involve placing those labeled bottles into cartons.

What Materials are Commonly Used in Secondary Packaging?
Secondary packaging materials vary widely, depending on the level of protection, cost-efficiency, and sustainability required. Common choices include corrugated cardboard, shrink film, and plastic wrap.
Common materials in secondary packaging include cardboard, shrink film, and plastic wrap, providing protection and sustainability options.
- Corrugated Cardboard: Ideal for boxes and trays due to durability and recyclability.
- Shrink Film: Offers moisture resistance and improved product visibility.
- Plastic Wrap: Provides additional durability, though eco-friendly alternatives are increasingly popular.
Each material serves a different purpose, influencing both production costs and the environmental impact of packaging.
Why Is Secondary Packaging Essential for Branding and Marketing?
Secondary packaging offers valuable branding opportunities, allowing companies to add logos, product information, and promotional messaging, which enhance product appeal and recognition on store shelves.
Secondary packaging provides space for logos, product information, and designs, strengthening brand identity and consumer appeal.
- Branding Space: Adds visual appeal through logos, product information, and color schemes.
- Shelf Presence: Helps products stand out, influencing purchasing decisions.
In retail settings, for example, a bottle labeling machine might apply attractive labels to individual items, but secondary packaging like branded cartons ensures cohesive presentation, reinforcing brand identity.
What are the Advantages of Using Secondary Packaging Machines?
Secondary packaging machines improve packaging processes by increasing speed, consistency, and reducing labor costs. These machines contribute to a smooth, efficient workflow, reducing material waste and ensuring reliable packaging quality.
Secondary packaging machines enhance speed, reduce labor costs, and improve product consistency for efficient packaging.
- Increased Efficiency: Automates tasks like packing and labeling, ensuring consistency.
- Cost Reduction: Minimizes labor costs and material waste.
For industries requiring high-volume packaging, such as food and beverages, using machines like shrink wrap machines ensures rapid, reliable processing that keeps up with demand.

What Role Do Secondary Packaging Machines Play in Supply Chain Management?
Secondary packaging machines enhance the efficiency of handling, organizing, and transporting products through the supply chain. By grouping items, these machines make storage and shipping easier and safer.
Secondary packaging machines improve logistics, streamline handling, and support efficient distribution within the supply chain.
- Inventory Management: Organizes products for quick access and storage.
- Distribution Efficiency: Packs items for easier stacking and safe delivery.
Efficient secondary packaging reduces the chances of product damage, supporting smoother inventory management and minimizing logistics costs.
How Do Secondary Packaging Machines Contribute to Sustainability?
Many secondary packaging machines now incorporate features to reduce waste and support eco-friendly packaging materials. Machines designed for precision allow companies to use minimal materials, supporting sustainable practices.
Secondary packaging machines reduce waste and support sustainable materials, contributing to eco-friendly packaging solutions.
- Material Optimization: Reduces excess packaging use, lowering costs and waste.
- Eco-Friendly Materials: Supports biodegradable films and recyclable options.
By choosing sustainable packaging methods, companies can minimize their environmental impact while maintaining high-quality packaging for their products.
Conclusion
Secondary packaging machines provide essential support for effective product handling, branding, and sustainability, enhancing product protection and appeal throughout the supply chain.