Improper food packaging leads to contamination, waste, and significant financial losses for businesses. Choosing the right packaging ensures food safety, extends freshness, and aligns with sustainability goals.
The different types of food packaging include flexible, rigid, semi-rigid, biodegradable, vacuum-sealed, modified atmosphere, aseptic, active, edible, and industrial bulk packaging. Each offers unique advantages for preservation, transport, and branding.
Discovering the right type of food packaging can revolutionize product safety, consumer appeal, and eco-conscious business practices.

Flexible Packaging
Flexible packaging is lightweight, versatile, and cost-effective. It includes pouches, laminated films, and plastic wraps commonly used for snacks, frozen foods, and single-serve beverages. Features like resealability, transparency, and custom branding options make it an excellent choice for businesses seeking modern, consumer-friendly solutions.
Example: A vacuum packaging machine can efficiently seal flexible pouches, enhancing freshness and prolonging shelf life for perishable goods.
Rigid Packaging
Rigid packaging provides excellent structural integrity and durability. Glass jars, cans, and hard plastic containers are ideal for sauces, canned foods, and beverages. This packaging type ensures long-term preservation and prevents contamination while offering reusable or recyclable options.
Example: A bottle filling machine works seamlessly with rigid containers to maintain precision in liquid products like juices and sauces.

Semi-Rigid Packaging
Semi-rigid packaging balances flexibility and rigidity, including paperboard cartons and molded pulp trays. Often used for bakery items, dairy products, and ready-to-eat meals, this type of packaging is cost-effective and recyclable, appealing to eco-conscious consumers.
Example: Flat labeling machines are often utilized to apply labels to semi-rigid packaging like cartons, ensuring a polished, professional look.
Biodegradable Packaging
Biodegradable packaging uses eco-friendly materials like plant-based plastics and compostable films. It aligns with sustainability goals, reducing environmental impact and appealing to green-conscious consumers.
Example: Honeycomb paper making machines help create biodegradable alternatives to traditional bubble wrap, offering sustainable protection for fragile goods.
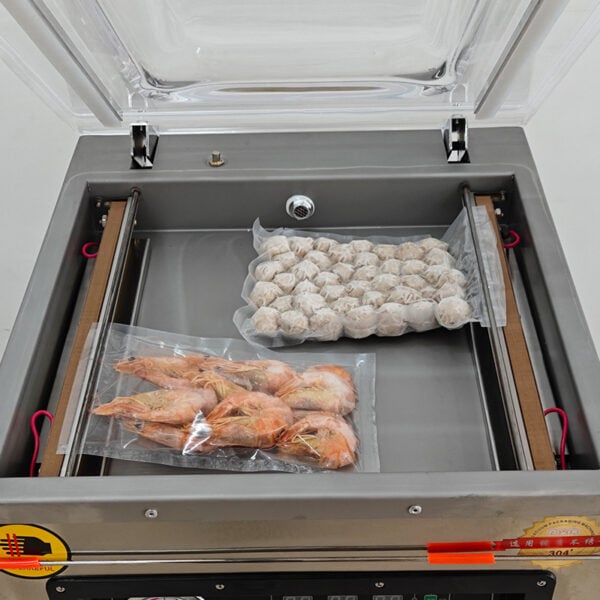
Vacuum-Sealed Packaging
Vacuum-sealed packaging eliminates air from the package, preserving freshness and extending the shelf life of perishable items like meats, seafood, and pre-cooked meals. This method also reduces space and transportation costs.
Example: Vacuum packaging machines automate this process, ensuring consistent sealing and quality.

Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP)
MAP packaging manipulates the atmospheric composition inside the package, often replacing oxygen with nitrogen or carbon dioxide. It is particularly effective for fresh produce, salads, and meats, maintaining quality for extended periods.
Aseptic Packaging
Aseptic packaging sterilizes both the product and the container, ensuring products like milk, juices, and sauces remain safe without refrigeration. It allows businesses to distribute items more efficiently across long distances.
Active Packaging
Active packaging includes features such as oxygen absorbers, desiccants, and moisture regulators that interact with the food to maintain its freshness. This packaging type is ideal for snacks, baked goods, and pharmaceuticals.

Edible Packaging
Edible packaging, such as seaweed-based wraps or gelatin coatings, offers innovative, waste-free solutions. It’s commonly used for desserts, beverages, and frozen treats, creating a unique consumer experience.
Industrial Bulk Packaging
For large-scale operations, industrial packaging, including drums, sacks, and pallets, facilitates the transport and storage of commodities like grains, sugar, and powders.
Example: Industrial shrink wrap provides secure, weather-resistant solutions for transporting bulk goods.
Conclusion
Effective food packaging ensures product safety, enhances shelf life, and meets consumer and sustainability demands, supporting both profitability and brand growth.