If you don’t package things right, it costs you money. If you don’t package things right, you get damaged goods. If you don’t package things right, you have shipping problems. If you don’t package things right, you have people complaining to you. A semi-automatic strapping machine can solve these problems without going to a fully automatic solution.
A semi-automatic strapping machine works by manually feeding the strap around the package. The machine then automatically tightens, seals, and cuts the strap, securing the package. Operators use controls like foot pedals to initiate the strapping process, combining manual input with automated efficiency.
You put the strap around the package, and the machine tightens it, seals it, and cuts it.

Key Components of a Semi-Automatic Strapping Machine
A semi-automatic strapping machine is built with key components that work together to secure packages efficiently. It features a tensioning mechanism, a sealing head, and manual feeding controls. The operator wraps the strapping material around the package and manually feeds the strap into the machine’s slot.
Once inserted, the packaging machine automatically pulls the strapping tight around the package. The tension is controlled by pre-set parameters to ensure consistent tightening, and a heat-sealing process binds the strap. Operators typically use a foot pedal to initiate the strapping process, allowing hands-free operation for managing packages.
This basic configuration enables the machine to deliver precise strapping without requiring full automation, making it ideal for businesses handling moderate packaging loads.
How Strapping is Applied
In a semi-automatic system, the operator is responsible for placing the strap around the package before feeding it into the machine. The machine takes over by automatically tensioning the strap according to pre-set levels, ensuring a snug fit around the package.
After the tensioning process, the machine seals the strap, often using a heat seal to bond the strap securely. The machine then cuts the strap, completing the packaging process. This combination of manual and automated steps provides an efficient and reliable solution for packaging operations.
Tensioning and Sealing Mechanism
The tensioning process is powered by an internal motor that applies uniform pressure to tighten the strap around the package. This ensures the package is securely held, preventing movement during transport.
After tensioning, the sealing head activates, using heat to bond the ends of the strap together. The heat seal forms a durable connection that won’t easily come undone, ensuring the package remains intact during shipping. The precision of the tensioning and sealing mechanisms helps maintain consistent results, even in high-volume packaging environments.
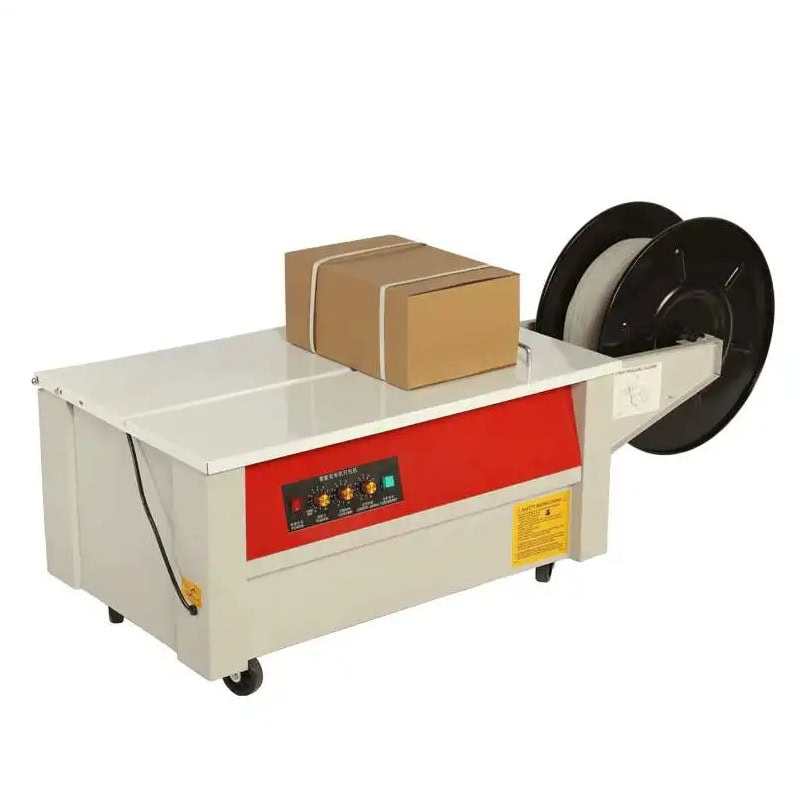

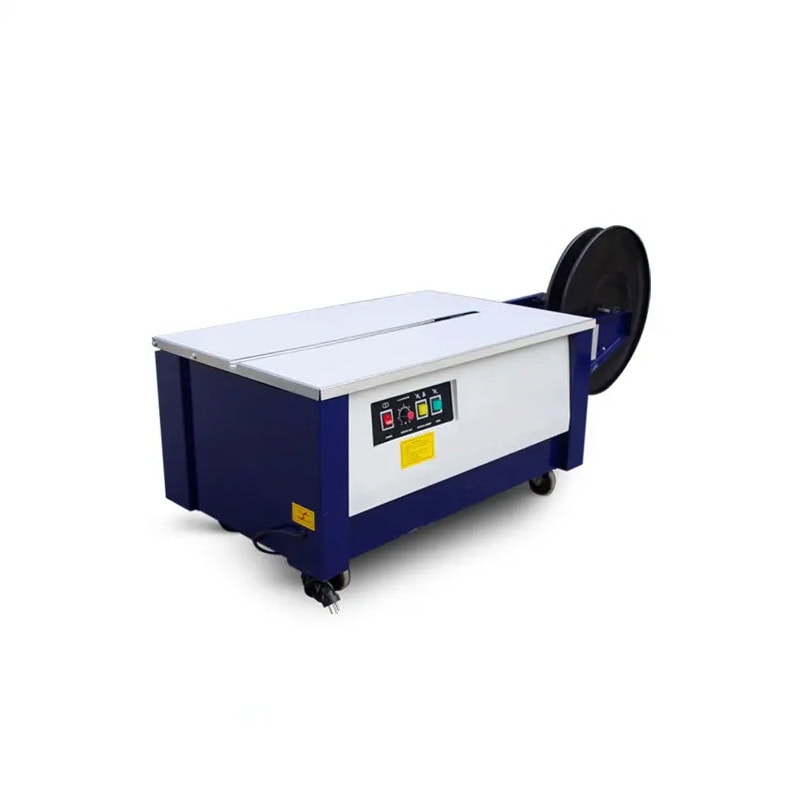
Applications of Semi-Automatic Strapping Machines
Semi-automatic strapping machines are widely used in industries where moderate packaging volumes are handled. These machines are ideal for logistics, manufacturing, and warehousing, where packages must be secured quickly but full automation may not be justified.
With the ability to accommodate various package sizes, semi-automatic machines are versatile, making them a popular choice for companies that handle diverse products, from boxes to irregularly shaped items.
Advantages Over Manual Strapping
Compared to manual strapping, semi-automatic machines significantly reduce the time and effort required to secure packages. Manual strapping can be labor-intensive and inconsistent, leading to variations in strap tension and potential package failures during shipping.
Semi-automatic machines ensure consistent tensioning and sealing, which improves package security. Operators can strap more packages in less time, leading to greater overall productivity.
Common Challenges and Solutions
While semi-automatic strapping machines are reliable, there are some common issues that operators may encounter. One of the most frequent problems is strap misalignment, where the strap does not feed correctly into the machine. Proper training and machine maintenance can help mitigate these issues.
Another common challenge is machine jams, often caused by improper feeding of the strapping material. Regular cleaning and timely part replacements can prevent these jams and keep the machine operating smoothly.
Maintenance of a Semi-Automatic Strapping Machine
Regular maintenance is essential for ensuring the long-term performance of a semi-automatic strapping machine. Key maintenance tasks include cleaning the sealing head, checking the tensioning components, and ensuring that all moving parts are properly lubricated.
It is also important to regularly inspect the machine for wear and tear, particularly in areas that handle the strapping material. Timely part replacements can prevent breakdowns and reduce downtime.
Safety Features of a Semi-Automatic Strapping Machine
Semi-automatic strapping machines are equipped with various safety features to protect operators. Most models include an emergency stop button, which allows the operator to immediately halt the machine if an issue occurs. Additionally, automatic shutoff mechanisms activate if the machine detects a problem during the strapping process.
These safety features help prevent accidents and ensure that the machine operates within safe parameters, protecting both the operator and the packages being strapped.
When to Use a Semi-Automatic Strapping Machine
Semi-automatic strapping machines are best suited for operations that handle moderate to high packaging volumes but do not require full automation. These machines strike a balance between manual control and automated efficiency, making them ideal for businesses looking to improve their packaging processes without the cost and complexity of fully automated systems.
For companies with varying package sizes and product types, semi-automatic machines provide the flexibility needed to handle diverse packaging tasks.
Cost Considerations
While the initial cost of a semi-automatic strapping machine is lower than that of fully automated machines, it still represents a significant investment. However, the machine pays for itself over time through increased productivity and reduced labor costs.
By automating key parts of the strapping process, businesses can process more packages in less time, reducing the need for manual labor and improving overall efficiency. This leads to a high return on investment, especially for companies that handle large volumes of packages regularly.
Conclusion
Semi-automatic strapping machines provide an affordable and efficient solution for businesses that need to secure packages with minimal manual effort. By automating the tensioning, sealing, and cutting processes, these machines reduce labor costs, improve consistency, and increase packaging speed.