Manual labeling processes often lead to inefficiency, errors, and inconsistent quality. These issues increase production costs and delay operations. Sticker labeling machines provide an automated solution to streamline the labeling process, delivering precision and efficiency.
How does a sticker labeling machine work?
Sticker labeling machines operate by unwinding a roll of labels, peeling them off the backing paper, and applying them precisely to products using a motorized system and sensor-controlled coordination. The PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) ensures seamless synchronization of the process.
Modern sticker labeling machines integrate advanced automation for efficiency and precision, making them indispensable in industries such as food, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals.
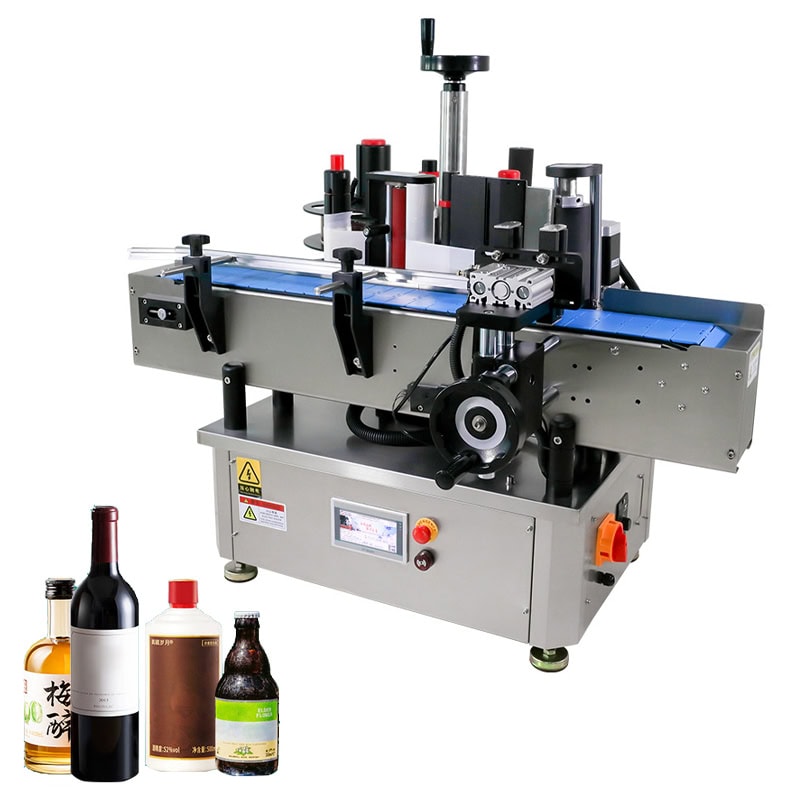

Overview of Sticker Labeling Machines
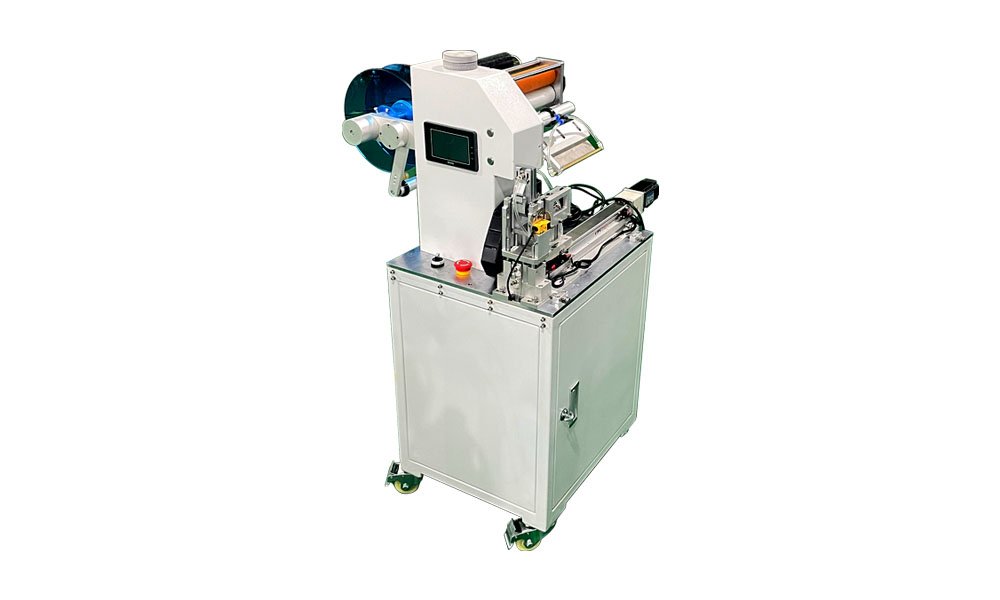
Sticker labeling machines are designed to automate the application of adhesive labels onto various products. They are categorized into manual, semi-automatic, and fully automatic models, depending on the degree of automation. These machines are widely used in industries such as food production, pharmaceuticals, and electronics.
Their versatility allows them to handle different product shapes and surfaces, such as cylindrical bottles, flat surfaces, and even corner edges, using specialized systems like the corner wrap labeling machine.
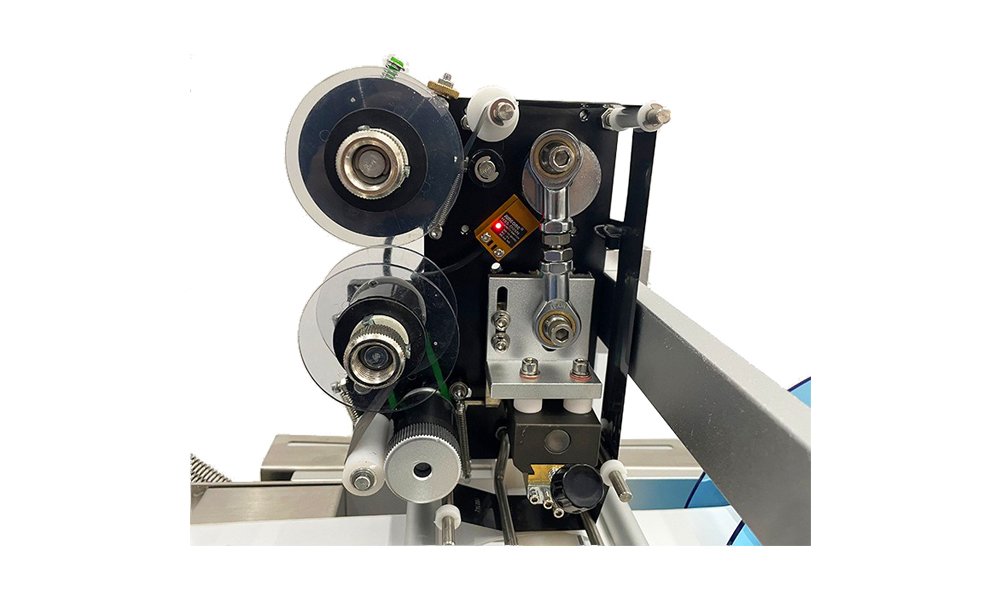
Key Components of a Sticker Labeling Machine
- Drive System: Includes motors, belts, and rollers to feed labels through the machine.
- Control System: A PLC processes input signals from sensors to manage precise label placement.
- Label Dispenser: Separates the label from the backing paper.
- Sensors: Detect product positioning and activate the labeling process.
- Application Mechanism: Uses rollers or arms to affix labels to products.
Working Principle
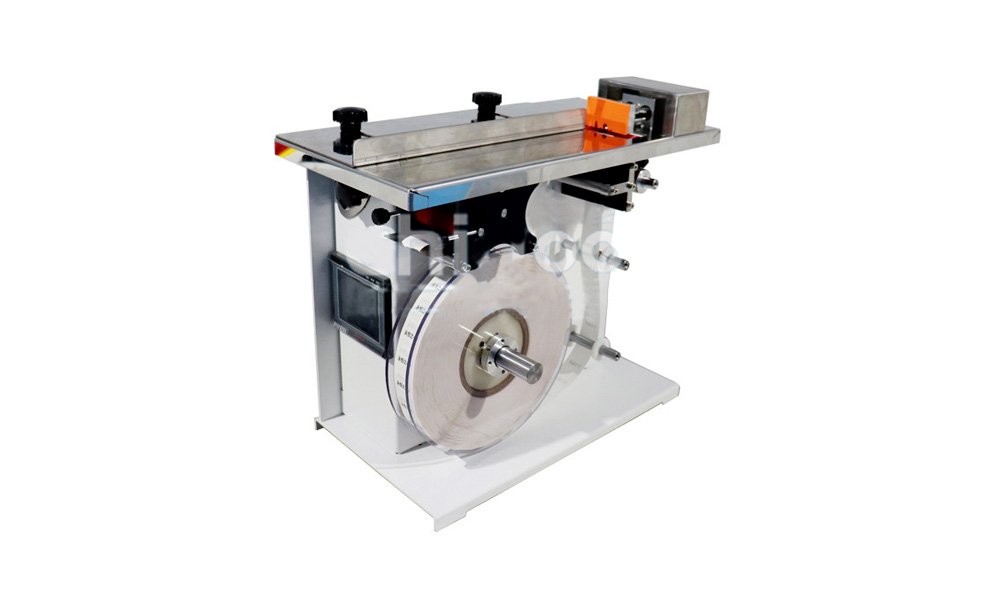
Sticker labeling machines rely on a combination of mechanical and electronic systems. The basic steps include:
- Unwinding and Peeling: Labels are fed from a roll, with the backing paper peeled away by a roller mechanism.
- Position Detection: Sensors identify the product’s exact position on the conveyor belt.
- Label Application: The PLC coordinates the application process, ensuring the label is affixed precisely to the product.
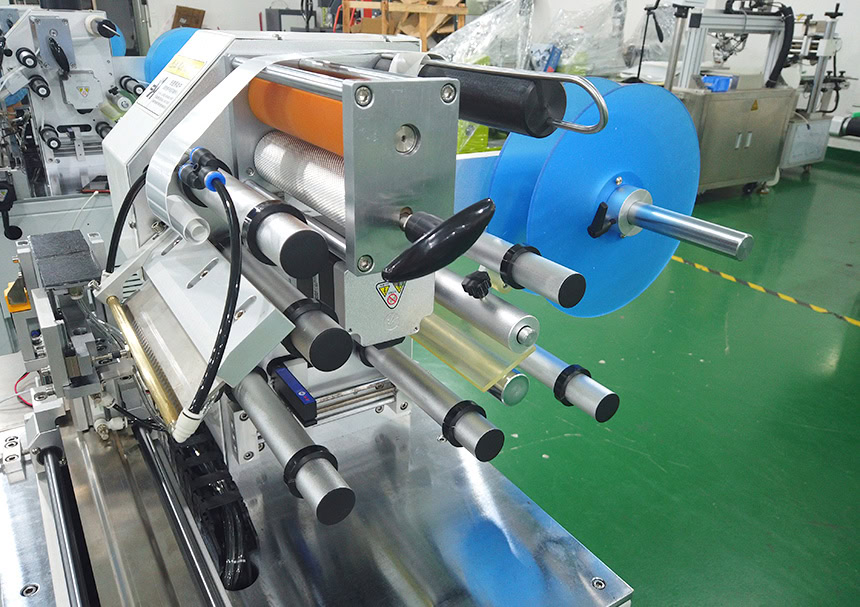

Label Application Process
- Peeling Stage: The label backing is separated to expose the adhesive layer.
- Positioning Stage: Products are aligned as sensors detect their placement.
- Application Stage: Labels are pressed onto products using rollers or an applicator arm for even adhesion.
Role of Sensors in Labeling Accuracy
Sensors play a crucial role in achieving accurate label placement. They detect the presence of products and labels, signaling the PLC to initiate or pause the labeling process. High-quality sensors, such as those used in industrial labeling systems, ensure precision for transparent or uniquely shaped labels.
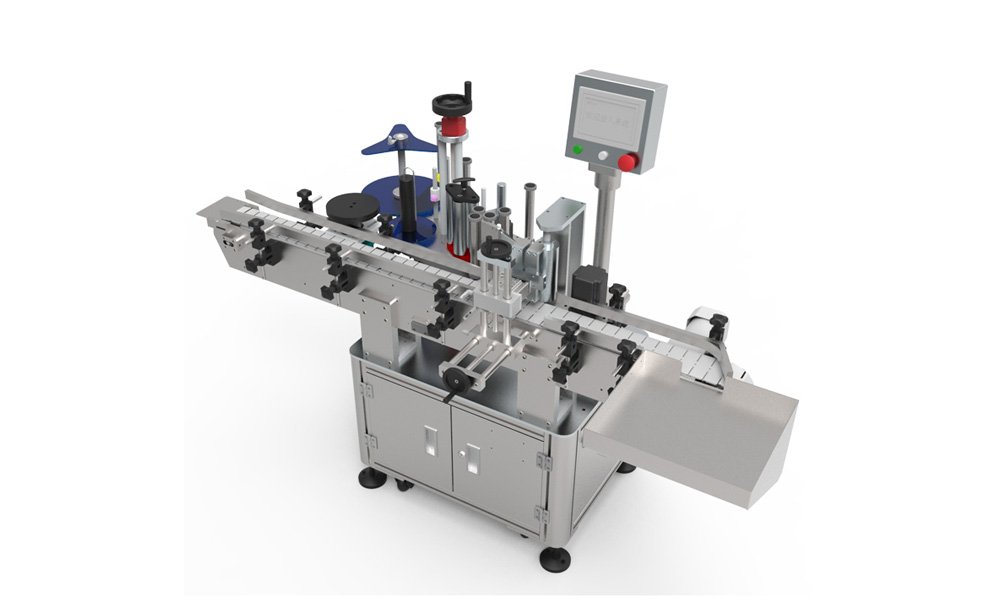
Types of Labeling Machines
- Cylindrical Surface Labelers: Ideal for labeling round bottles and jars.
- Flat Labeling Machines: Used for boxes and flat surfaces.
- Corner Wrap Labelers: Designed for labels that need to wrap around edges or corners.
Each type caters to specific product needs, such as the rolling bottle labeling machine for cylindrical bottles or flag labeling machines for wire or cable applications.
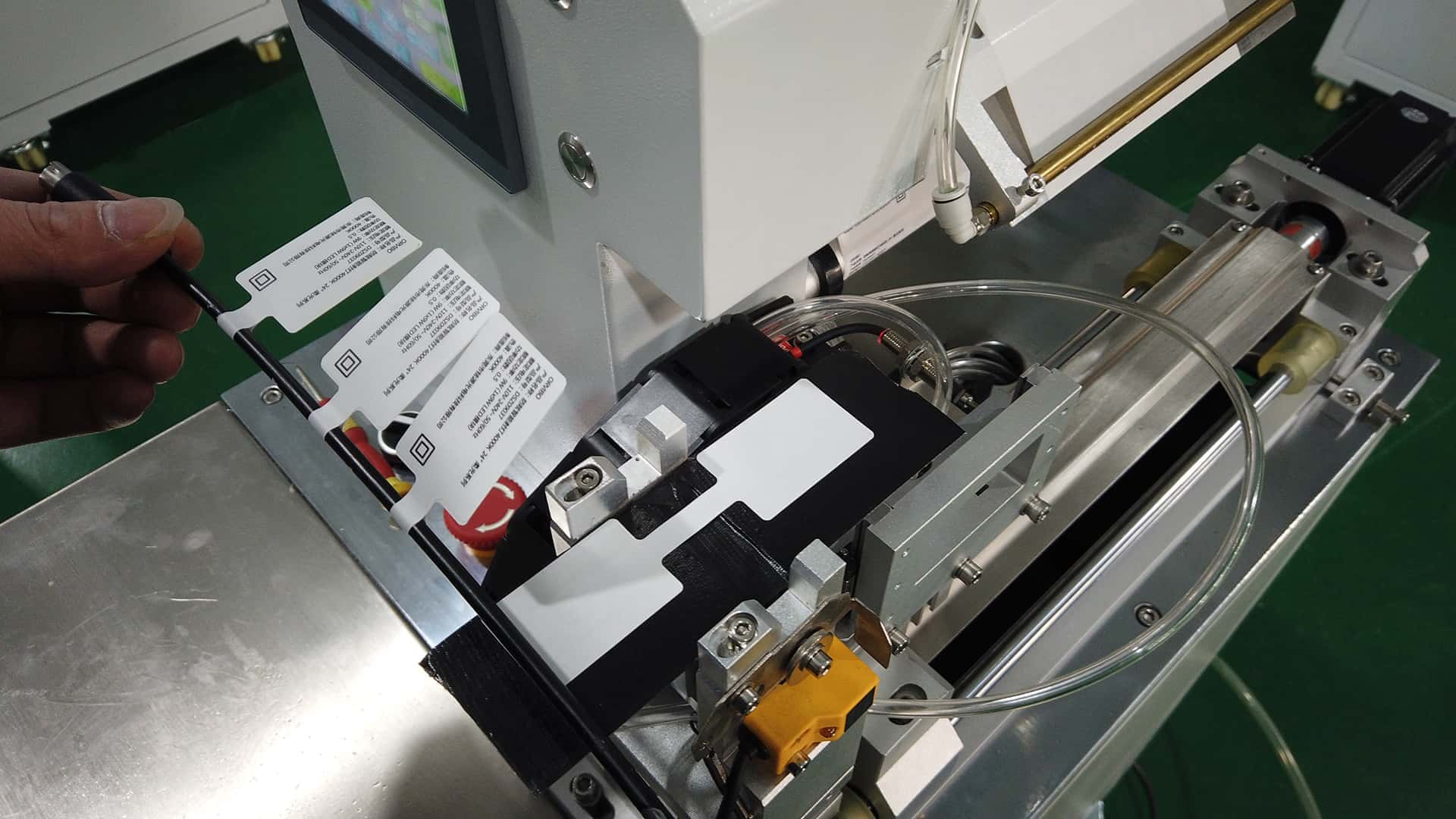

Automation and PLC Integration
The PLC acts as the brain of the machine, synchronizing product movement with label application. Features like speed adjustment, delay timing, and error detection are programmed into the system to enhance functionality and ensure efficiency in high-speed production environments.
Advantages of Sticker Labeling Machines
- High Accuracy: Placement precision up to ±0.5mm minimizes errors.
- Increased Speed: Models can handle up to 1,500 pieces per hour, improving throughput.
- Consistency: Automated systems provide uniform labeling quality.
- Versatility: Machines are adaptable for various product shapes and sizes.
Maintenance and Calibration
Regular maintenance ensures optimal machine performance. Key tasks include:
- Cleaning Sensors and Rollers: Prevents debris from disrupting operations.
- Recalibrating Sensors: Adapts the machine to different label sizes or product dimensions.
- Alignment Checks: Ensures smooth feeding and label placement.
Applications Across Industries
Sticker labeling machines are integral to multiple industries. For example:
- Food Industry: Labels for bottles, jars, and packages.
- Cosmetics: High-quality labeling for bottles and containers.
- Electronics: Barcode labeling for devices and components.
In packaging lines, these machines often complement systems like bottle filling machines and industrial shrink wrap solutions for a comprehensive production process.
Conclusion
Sticker labeling machines are pivotal in modern manufacturing, providing accuracy, efficiency, and scalability. Their integration with automated systems ensures smooth operations across diverse industries, enhancing productivity while reducing operational costs.