Induction sealing is essential for creating airtight seals, but using incompatible materials can lead to leaks, product damage, or contamination. Selecting the correct materials ensures durability and reliability in packaging.
Induction sealing materials include aluminum foil, heat-seal layers (polyethylene, polypropylene, PET), pulpboard, wax, and adhesives. These materials work together to create an airtight, tamper-evident seal compatible with containers like glass and plastic.
Let’s explore the specific materials, their functions, and how they contribute to effective induction sealing.
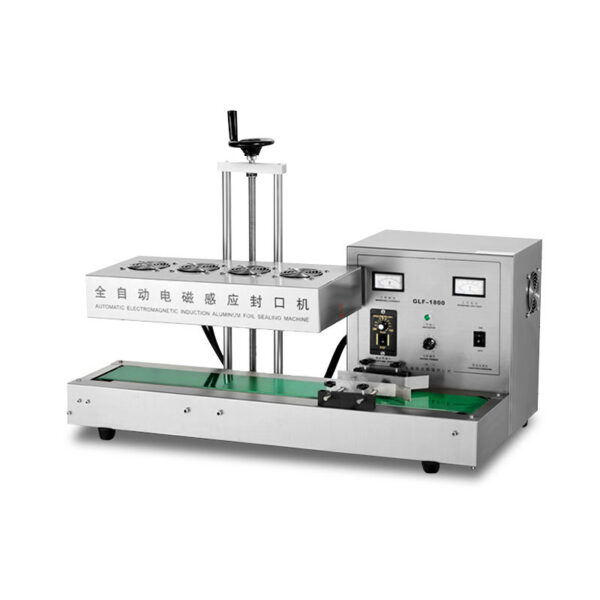

What is Induction Sealing?
Induction sealing uses electromagnetic induction to bond a foil seal to container rims, ensuring leak-proof and tamper-evident packaging.
How It Works
Induction sealing applies electromagnetic energy to heat an aluminum foil liner. The liner is made of multiple layers:
- Aluminum Foil: Absorbs heat to melt the sealant.
- Heat-Seal Layer: Polyethylene or polypropylene adheres to the container.
- Wax Layer and Pulpboard: Provide bonding and structural support.
This method is compatible with containers such as plastic (HDPE, LDPE, PET) and glass. It is widely used in industries requiring reliable seals, such as for induction sealing machines.
What Are the Components of Induction Seal Materials?
Induction seals consist of an aluminum foil layer, heat-seal material, pulpboard, wax, and adhesive to ensure airtight seals.
Material Composition
| Layer | Function |
|---|---|
| Aluminum Foil | Heating element for the sealing process |
| Heat-Seal Layer | Bonds to the container rim |
| Wax | Binds the foil to the backing |
| Pulpboard/Backing | Provides structural stability |
Each layer plays a critical role in forming a durable seal. Customization allows compatibility with specific packaging, such as those used in customized labeling machines.
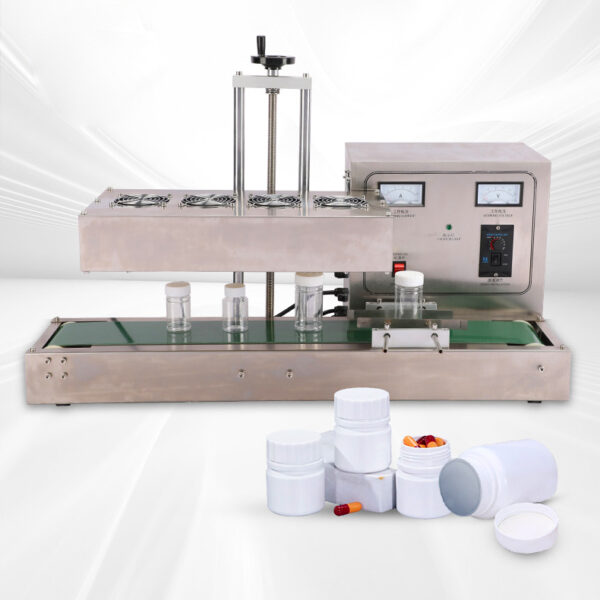

What Types of Containers Work with Induction Seals?
Induction seals are compatible with glass containers and plastic containers made of PET, HDPE, LDPE, and PP.
Compatibility Factors
- Plastic Containers: Require heat-seal layers matched to the resin type (e.g., PET).
- Glass Containers: Need specialized adhesives in the liner to ensure a strong bond.
The success of induction sealing also depends on clean rims and precise alignment during the sealing process. Packaging industries use filling machines and sealing machines together for maximum efficiency.
How Do Induction Sealing Machines Work?
Induction machines use electromagnetic waves to generate heat in an aluminum liner, melting the sealant to bond to the container rim.
Key Components of an Induction Sealing Machine
| Part | Function |
|---|---|
| Induction Coil | Generates electromagnetic energy |
| Power Supply | Provides adjustable energy levels |
| Conveyor System | Moves containers under the sealing head |
Precise control of power output, pressure, and time is essential to achieve high-quality seals. Sealing machines often operate alongside bottle labeling machines in production lines.
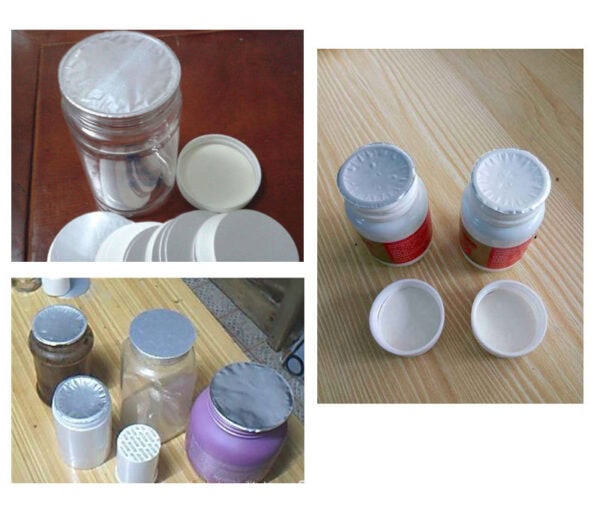

Why Is Induction Sealing Essential in Packaging?
Induction sealing enhances product safety, shelf life, and tamper evidence, making it vital for various industries.
Benefits of Induction Sealing
- Tamper Evidence: Ensures consumer trust.
- Leak Prevention: Protects products during transit.
- Versatile Applications: Suitable for food, beverage, and pharmaceutical packaging.
Companies use induction sealing with complementary machines like powder filling machines to streamline packaging processes and maintain quality.
Conclusion
Selecting the right induction sealing materials—aluminum foil, heat-seal layers, wax, and pulpboard—ensures durable, tamper-evident packaging for diverse container types. Careful calibration and material compatibility are key.