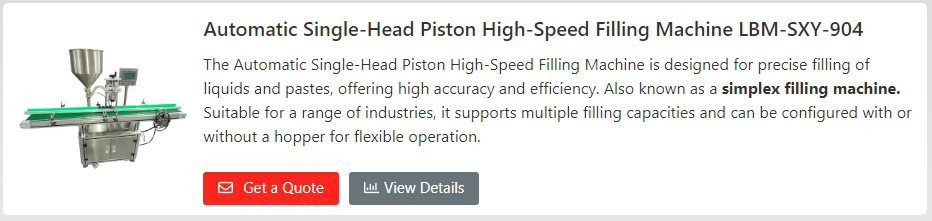
Calculating fill time correctly in an injection molding machine is critical to maintaining quality and keeping your operation running. Mess this up, and you’ll have all kinds of defects and higher costs. Understand the formula and how to apply it to prevent those problems.
To calculate the fill time, divide the mold volume by the material flow rate. You’ll need to adjust for material type and mold complexity to get the best results.
Knowing how to optimize your fill time will give you better parts and make your operation more efficient.

The Importance of Fill Time in Injection Molding
Fill time is the duration required for molten plastic to fill the mold cavity in an injection molding machine. It is critical to maintaining part quality and process consistency. If the fill time is too short, defects like air traps and warpage may occur, while too long of a fill time can result in incomplete parts or sink marks.
Balancing fill time is essential to ensure the parts are fully formed without compromising the integrity of the material or the final product’s appearance.
Key Factors Influencing Fill Time
Several factors contribute to the fill time in injection molding:
1. Material Properties
Different materials have varying viscosities and flow rates. For example, highly viscous materials such as polycarbonate will take longer to fill the mold compared to low-viscosity materials like polypropylene. Material datasheets provide information about flow rates and should be referenced when calculating fill time.
2. Mold Design
The complexity of the mold design greatly affects fill time. Molds with intricate geometries, thin walls, or multiple cavities require more time to fill evenly. Optimizing mold design and making allowances for complex parts can help streamline the fill time.

The Formula for Calculating Fill Time
The basic formula to calculate fill time is:
Fill Time = Mold Volume / Material Flow Rate
This simple formula is foundational but may need adjustments based on material properties, mold complexity, and the type of injection molding machine used.
- Mold Volume: The volume of the cavity to be filled, measured in cubic centimeters.
- Material Flow Rate: The rate at which the molten material flows, usually given in cm³/s.
Using this formula allows for a straightforward calculation of how long the machine will take to fill the mold cavity. However, each component of the formula must be measured or estimated accurately to ensure precision.
Adjusting Fill Time Based on Material Flow Rate
The flow rate of the material depends on its viscosity and how it behaves under heat and pressure. For example:
- Low-viscosity materials: These materials flow easily, requiring shorter fill times.
- High-viscosity materials: These materials flow slower and will require longer fill times to completely fill the mold cavity.
Injection speed and pressure adjustments can help balance fill time, especially when dealing with complex materials or product designs.
Mold Design Considerations for Fill Time
The design of the mold plays a significant role in fill time calculation. For example, molds with thin walls or multiple cavities will require careful fill time adjustments to ensure uniformity across the entire mold. Uneven fill times can result in defective parts, so it’s crucial to ensure that each cavity fills at the same rate.
Using computer-aided engineering (CAE) tools such as Moldflow Analysis can simulate the fill process, offering more accurate fill time predictions for complex mold designs.

Incorporating Injection Pressure into Fill Time Calculations
Injection pressure is another critical factor in determining fill time. Increasing pressure can reduce fill time by forcing the material into the mold faster, but excessive pressure can lead to defects such as flashing or short shots. Balancing the pressure with the flow rate is essential to achieve the correct fill time without compromising part quality.
Monitoring and adjusting pressure in real-time is recommended to maintain consistent fill times across production runs.
The Role of Mold Temperature in Fill Time
Mold temperature affects material viscosity, which in turn influences fill time. Higher temperatures lower the viscosity of the material, allowing it to flow faster and reducing fill time. Conversely, lower temperatures increase viscosity, slowing the flow and extending the fill time.
Proper temperature control is necessary to maintain consistent fill times and ensure optimal part quality.
Utilizing Software Tools for Accurate Fill Time Calculation
Advanced software tools like Moldflow and Cycle Time Calculators allow engineers to simulate the entire injection molding process, including fill time. These tools account for material properties, mold design, temperature, and pressure, providing a more accurate estimation of the fill time.
Using such tools helps avoid guesswork and ensures that the calculated fill time matches the real-world production environment.

Practical Tips for Optimizing Fill Time
- Start with Material Datasheets: Always begin with the recommended flow rates and injection pressures provided by the material manufacturer.
- Conduct Moldflow Simulations: Simulations provide a clear view of how the material will behave during the filling process, helping fine-tune fill time.
- Monitor Fill Time Continuously: Use real-time monitoring systems to adjust fill time based on actual machine performance.
Following these practices will help ensure that fill time is optimized, leading to improved product quality and increased operational efficiency.
Conclusion
Accurately calculating the fill time in an injection molding machine is essential to achieving consistent production quality and optimizing the manufacturing process. By using the correct formula and adjusting for material properties, mold design, and machine settings, manufacturers can optimize their injection cycles and reduce production errors.
You may be interested in: