Inefficient packaging processes can lead to bottlenecks, increased costs, and product damage, affecting profitability and customer satisfaction. Implementing advanced packaging machinery ensures consistent, high-quality packaging, minimizes waste, and optimizes productivity.
Packaging machinery automates the handling, sealing, and labeling processes by integrating multiple mechanisms such as conveyors, sensors, and programmable controllers to enhance precision and efficiency across diverse packaging tasks.
Read on to explore the essential components, working principles, and types of packaging machinery.
Introduction to Packaging Machinery
Packaging machinery is a broad category of equipment designed to automate packaging tasks like filling, sealing, labeling, and wrapping. The advent of automation in packaging is critical to maintaining quality control, ensuring product protection, and enhancing production speed. From large-scale manufacturers to specialized industries, packaging machines such as labeling machines, filling machines, and shrink wrap machines have become indispensable tools.

Core Components of Packaging Machinery
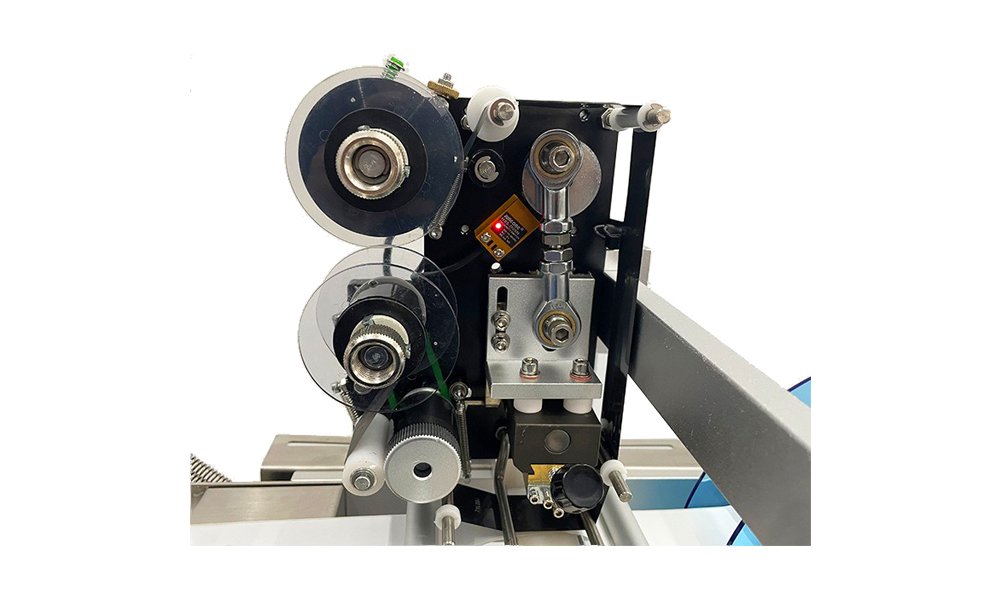
Mechanical Parts
The core components of any packaging machine include conveyors, capping units, filling heads, and sealing mechanisms. Conveyors guide products through each stage, while capping and filling units precisely manage the product’s containment. Sealing mechanisms, whether heat or adhesive-based, ensure that products are securely packaged to meet quality standards.
Sensors and Detection Systems
Modern packaging machinery relies heavily on sensors to maintain accuracy. Sensors, such as electric eyes, detect the position of each product, ensuring correct label placement and packaging integrity. They also assist in quality checks, automatically discarding products that do not meet set specifications, thus reducing waste.
PLC Systems
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are essential for controlling and monitoring each function of a packaging machine. These systems allow operators to set specific parameters, adjust speed, and switch between manual and automated operations, making it easier to adapt to different product sizes and packaging types.
Types of Packaging Machinery
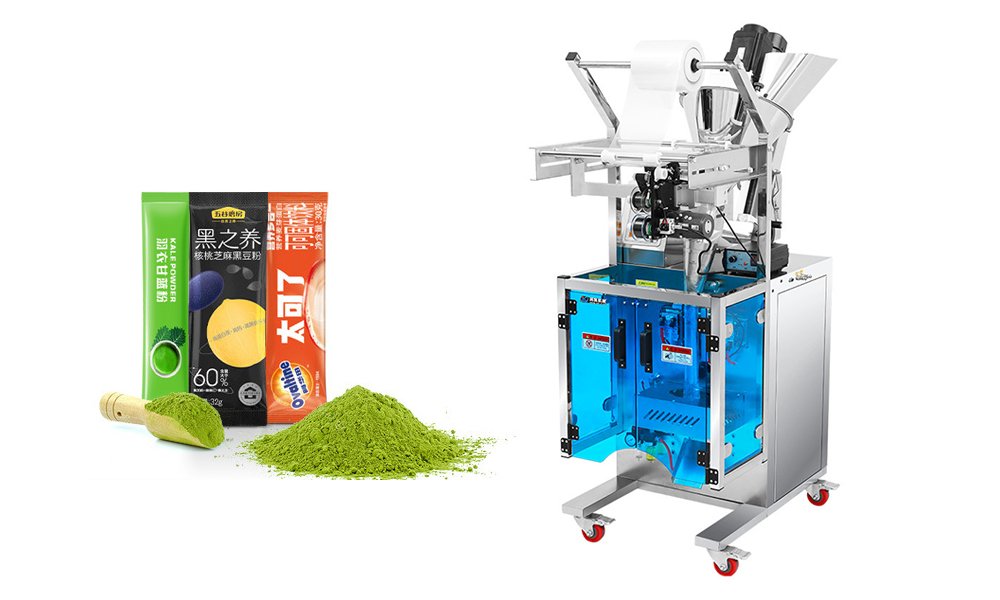
Filling Machines
Filling machines, such as Liquid Filling Machines and Powder Filling Machines, are designed to measure and fill liquids, powders, or granules with precision. Different filling methods include volumetric filling, gravimetric filling, and vacuum filling, each suited to specific product characteristics. These machines prevent spillage and maintain accurate product quantity, critical for consumer trust and regulatory compliance.
Sealing Machines
Sealing machines apply various techniques, such as heat, pressure, or adhesives, to ensure that each package is tightly closed. Heat sealers are common for plastic pouches, while adhesive-based machines are ideal for cardboard and paper packaging. Sealing maintains product freshness and protects against contamination.
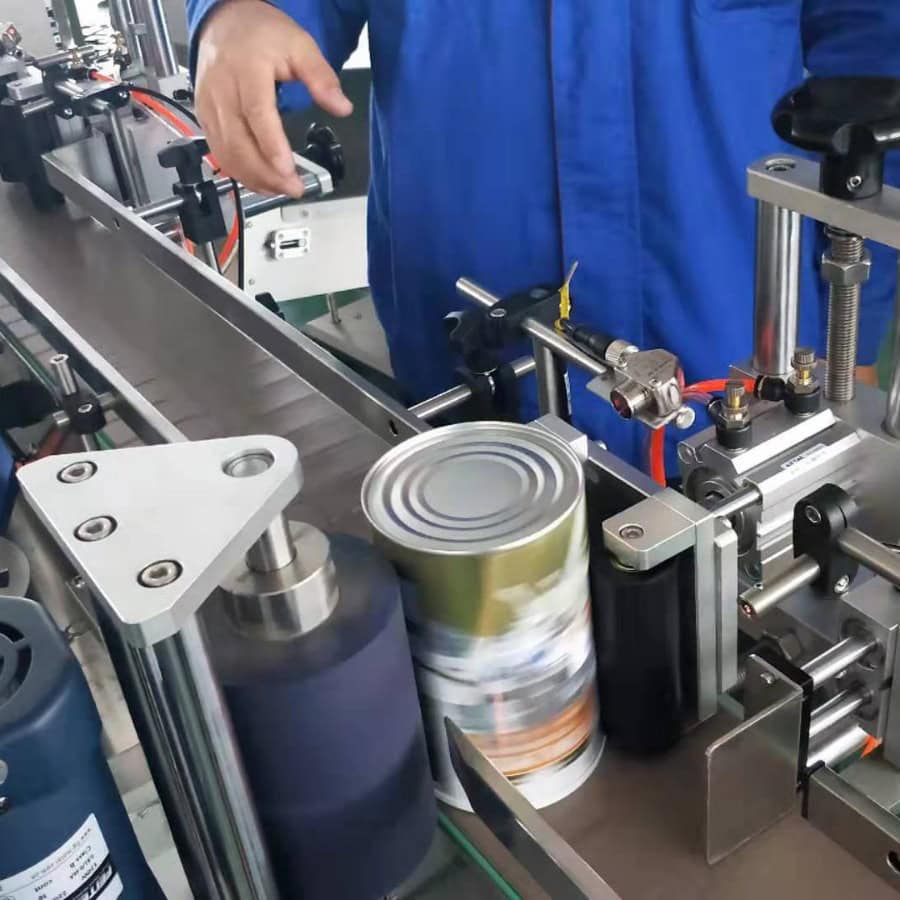
Labeling Machines
Labeling machines, such as Flag Labeling Machines and Bottle Labeling Machines, apply labels accurately to products. Labels serve various purposes, from brand recognition to regulatory information. Advanced labeling machines use electric eyes to detect product positioning, ensuring precise label placement. Customized labeling solutions are also available for products with irregular shapes, enhancing brand presentation and compliance.
Wrapping and Bundling Machines
Wrapping machines use shrink wrap or film to bundle products for storage or transport, providing an extra layer of protection. Bundling ensures items remain organized, reducing damage during shipment and allowing bulk handling. Shrink wrap machines use heat to conform plastic tightly around products, making them ideal for industries focused on appearance and protection.

Working Principles of Key Packaging Machines
Bagging Machines
Bagging machines handle products in bags, pouches, or sacks. The process includes filling, sealing, and discharging, with automated bagging machines capable of high-speed operations. Products such as grains, powders, and pet food are often bagged, where the machine ensures consistent weight and seal integrity.
Vacuum Packaging Machines
Vacuum packaging machines remove air from a package before sealing it, extending product shelf life by reducing oxidation. The process is widely used in food industries to maintain freshness and prevent spoilage. The machine creates an airtight seal, which also enhances package durability during shipping.
Pouch Packaging Machines
Pouch packaging machines fill and seal products in pouches, a popular format for convenience and cost-efficiency. They are equipped to handle both liquid and solid contents, and the sealing process typically includes heat-sealing, ensuring a leak-proof closure. Industries use pouch packaging for everything from snacks to detergents due to its versatile and consumer-friendly design.
Role of Packaging Machine Operators
Operators play a crucial role in setting up, monitoring, and adjusting packaging machinery. They are responsible for machine calibration, ensuring the correct fill levels, label positioning, and adherence to quality standards. Skilled operators can identify malfunctions, making adjustments in real-time to prevent production delays and maintain product consistency.

Automated Packaging Processes
An automated packaging process consists of a series of precise, pre-programmed actions controlled by a PLC system. The process starts with loading and moves through filling, sealing, and labeling to a quality control checkpoint. Automation benefits include faster production times, lower labor costs, and reduced contamination risks, vital for sectors such as food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics.
Working Principle of Sensors and Electric Eyes
Sensors and electric eyes play a pivotal role in maintaining the accuracy of packaging machinery. They detect product and label positions, control conveyor speed, and help machines adjust to variations in product sizes or shapes. Electric eyes work by emitting a beam that identifies the correct label placement, signaling the machine to initiate labeling or other designated actions. Sensors are essential in preventing misalignment and maintaining consistent packaging quality.
Packaging Machinery Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance is key to extending the life of packaging machinery. Operators should routinely inspect and clean components, calibrate sensors, and test PLC settings to prevent breakdowns. Troubleshooting common issues—such as sensor misalignment, conveyor speed fluctuations, and sealing inconsistencies—ensures smooth production and minimizes costly downtime.
Future Trends in Packaging Machinery
The future of packaging machinery is leaning toward smarter, more sustainable solutions. Smart packaging technology, such as IoT-connected devices, enables remote monitoring and predictive maintenance. Machine learning applications help packaging systems adapt to product variations, improving efficiency and accuracy. Additionally, sustainability-focused machines are designed to minimize energy consumption and work with recyclable materials.
Conclusion
Packaging machinery enhances productivity, ensures product safety, and supports branding through automated and precise operations. Embracing advanced technology in packaging is essential for manufacturers to remain competitive and deliver high-quality products efficiently.