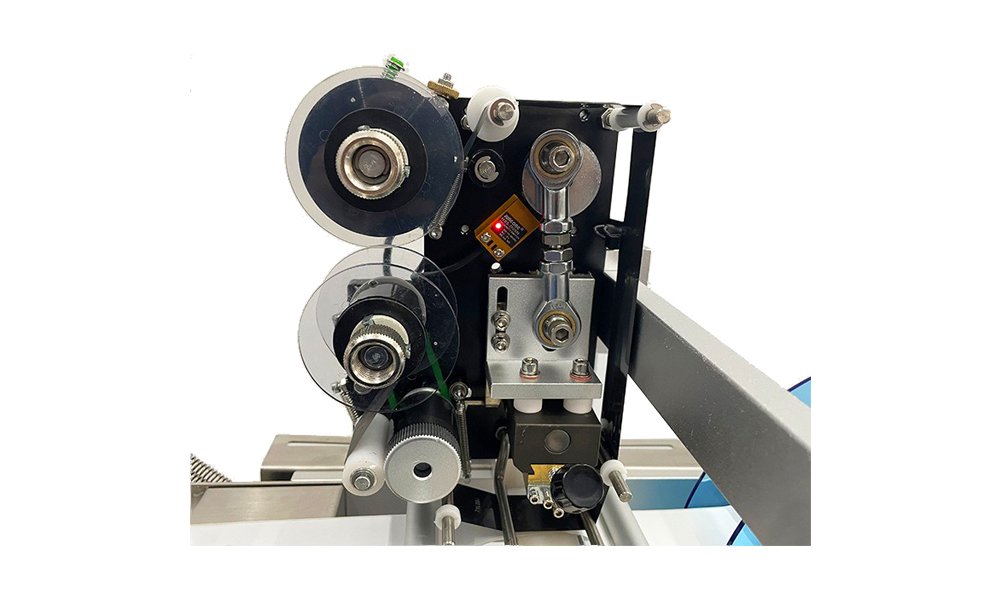
Struggling with manual labeling can lead to operational delays and inconsistencies. Incorrect labeling affects brand image and compliance. A label printing machine is the solution for speed, accuracy, and efficiency.
Label printing machines work by using advanced systems like thermal, inkjet, or laser technologies to apply labels precisely on products. Their design includes feeding, peeling, and applying mechanisms for consistent results.
Dive deeper to explore the working mechanisms, technologies, and efficiency of label printing machines.

Basic Functionality of Label Printing Machines
Label printing machines are automated or semi-automated devices designed to apply labels on a wide range of surfaces. By integrating precise mechanisms, these machines streamline the process of attaching labels while minimizing human error. Core functionalities include feeding the labels, aligning them accurately, and applying them to products in sync with production lines.
These machines are compatible with various industries, such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and electronics. For businesses using specialized solutions like rolling bottle labeling machines or flag labeling machines, efficiency and consistency are dramatically improved.
Key Components and Their Roles
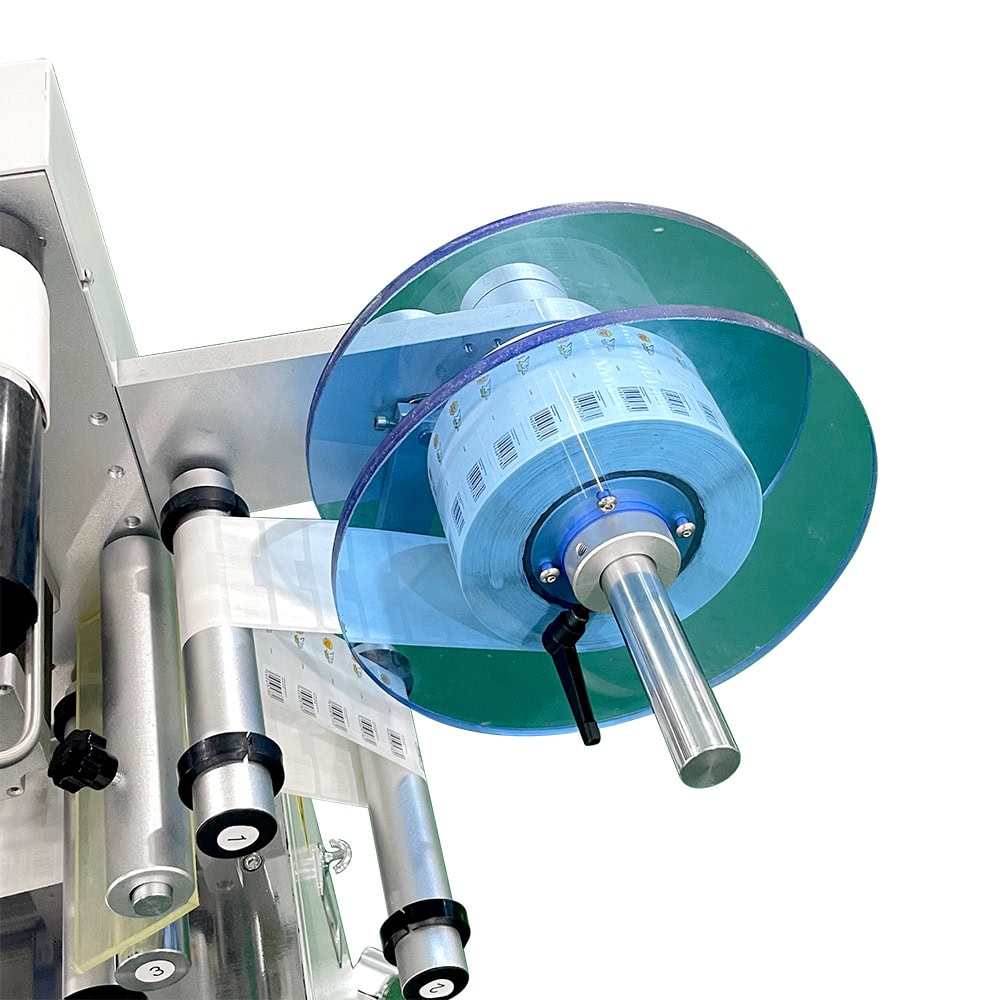
Label Feed System
The label feed system ensures the continuous delivery of labels to the peeling mechanism. Labels are typically stored in rolls or stacks and are guided through rollers to maintain tension and alignment.
Peeling Mechanism
The peeling mechanism separates the label from its backing paper, positioning it precisely for application. Adjustments can be made for different label sizes and product shapes, ensuring versatility in application.
Sensors and Control System
Sensors play a critical role in detecting both product position and label availability. These sensors feed signals to the control system, often a PLC (Programmable Logic Controller), which ensures precise timing for label application.
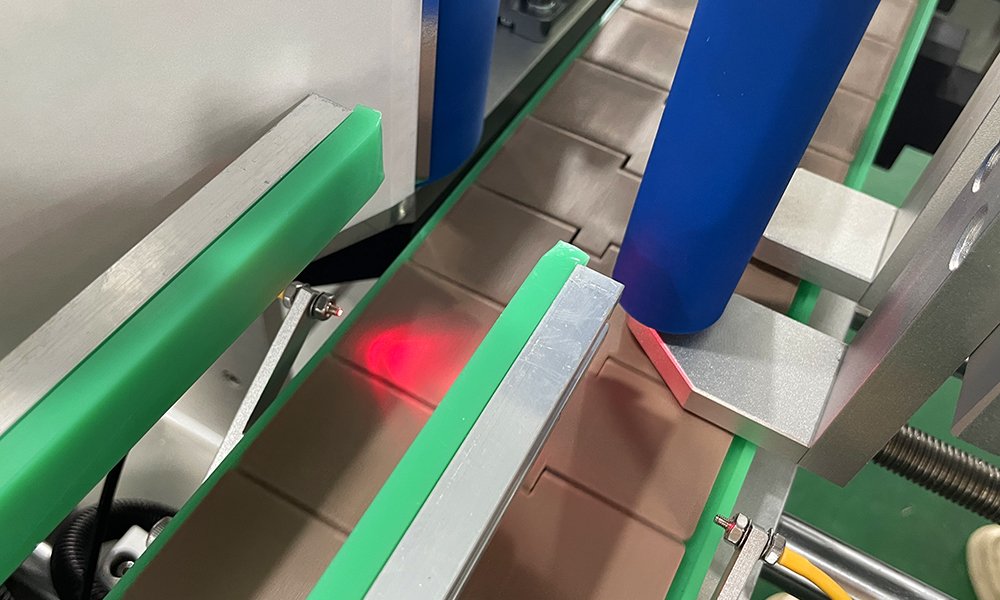

Label Printing Techniques
Label printing machines employ various printing technologies, depending on the application and budget:
- Thermal Printing: Uses heat to transfer ink onto labels, ideal for shipping labels and barcode printing.
- Inkjet and Laser Printing: Perfect for high-resolution, detailed designs, often used in branding and promotional labels.
Some machines, such as industrial label printers, combine these technologies for specialized tasks, offering businesses flexibility in labeling operations.
How Labels Are Applied
The labeling process generally follows these steps:
- Product Detection: Sensors identify the presence and position of the product.
- Label Dispensing: The machine releases a label from the roll.
- Adhesive Activation: Adhesives are applied or heat-activated, depending on the label type.
- Label Application: Rollers or applicator arms press the label onto the product, ensuring a firm attachment.
This process is highly adaptable, enabling the application of labels on flat, curved, or cylindrical surfaces.
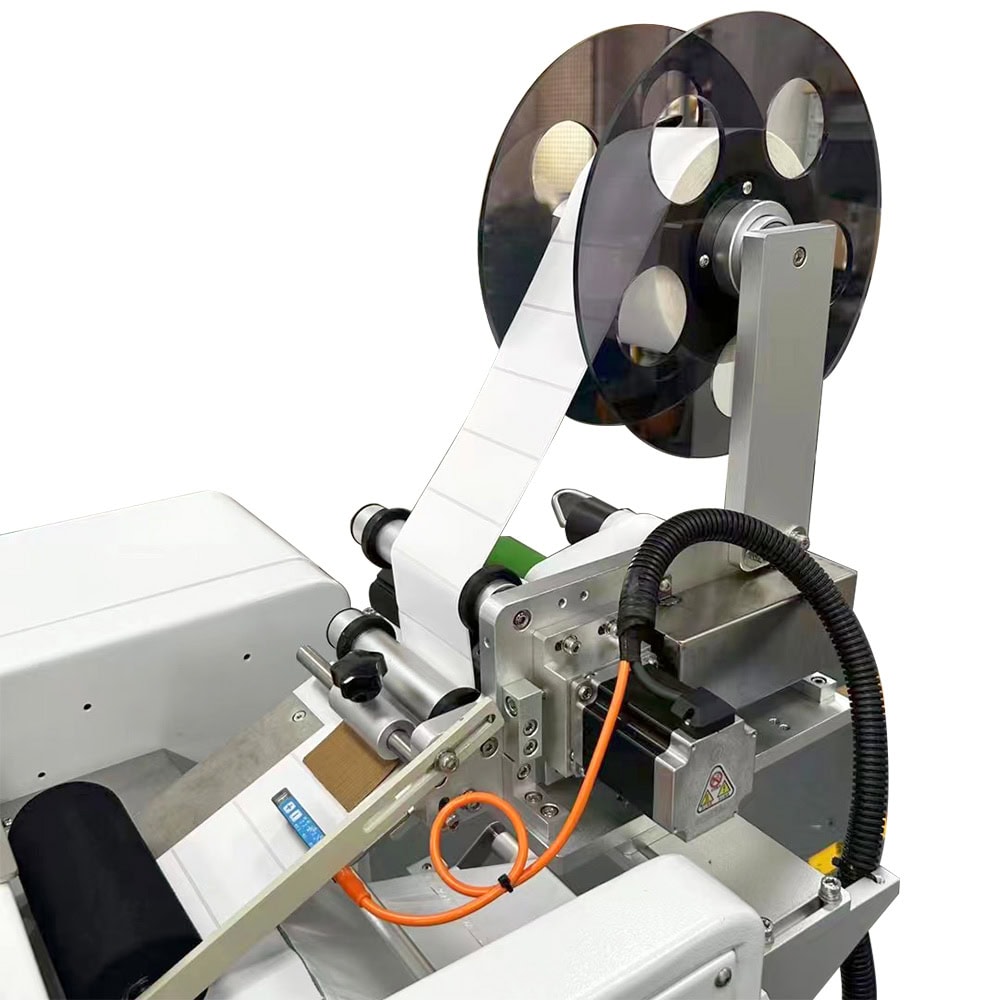
Automation and Integration in Production Lines
Modern label printing machines integrate seamlessly into automated production lines. By working in tandem with other equipment like filling machines or packaging machines, they contribute to a fully synchronized workflow. Many advanced models allow for easy parameter adjustments through touchscreen interfaces, ensuring compatibility with various production requirements.
Role of Electric Sensors
Electric sensors are vital for maintaining synchronization between the label and product. These sensors detect gaps between labels and monitor product movement. Adjustments to these sensors ensure the precision of labeling, reducing errors in high-speed operations.
Differences Between Label Makers and Printers
Label makers are typically small, portable devices for creating simple labels, while label printers are industrial-grade machines designed for large-scale production. Label printers are ideal for businesses needing consistent, high-quality labels in high volumes.

Importance of Maintenance and Calibration
Regular maintenance is crucial for the longevity and performance of label printing machines. Cleaning rollers, checking sensors, and replacing worn parts are essential practices. Additionally, periodic calibration corrects print positions and ensures precise application. For detailed guidance on calibration, businesses can refer to instructions tailored for specific models, such as industrial or barcode printers.
Benefits of Label Printing Machines
Label printing machines enhance productivity, reduce operational errors, and ensure compliance with industry standards. They offer high-speed labeling capabilities, saving valuable time in production environments. Integration with systems like automatic liquid packaging machines adds further value to manufacturing setups.
Popular Applications Across Industries
Label printing machines find applications in diverse industries, from pharmaceuticals to food packaging. They are essential for tasks such as labeling honeycomb paper products, marking batch codes, or branding on product surfaces. Their adaptability and precision make them indispensable tools in modern manufacturing.
Conclusion
Label printing machines streamline labeling with precision and speed. Understanding their mechanisms empowers businesses to choose the right solution for their operations. Learn more about how our range of labeling machines can meet your specific needs.