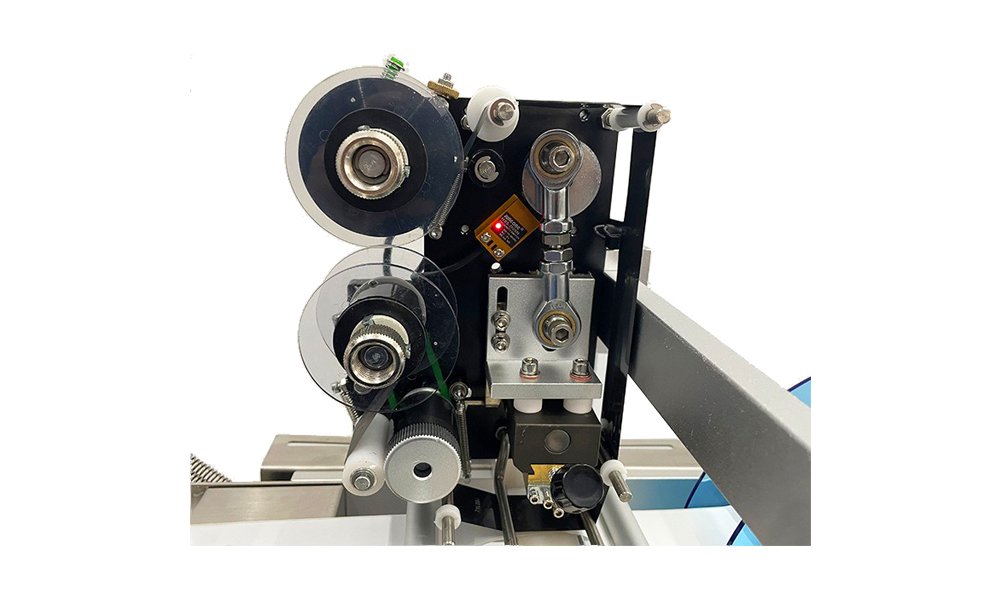
Many companies in the food, pharmaceutical, and beverage industries rely on induction sealers for secure packaging. However, there is often concern about the safety of these machines. If not used properly, induction sealers could pose risks such as contamination or improper seals, which could compromise product integrity and consumer safety.
Induction sealers are safe when used correctly. They provide tamper-evident seals, enhance product integrity, and extend shelf life. However, incorrect usage or poor maintenance could lead to safety concerns.
Let’s take a closer look at the mechanisms of induction sealing, its safety benefits, potential risks, and how to ensure safe operation.
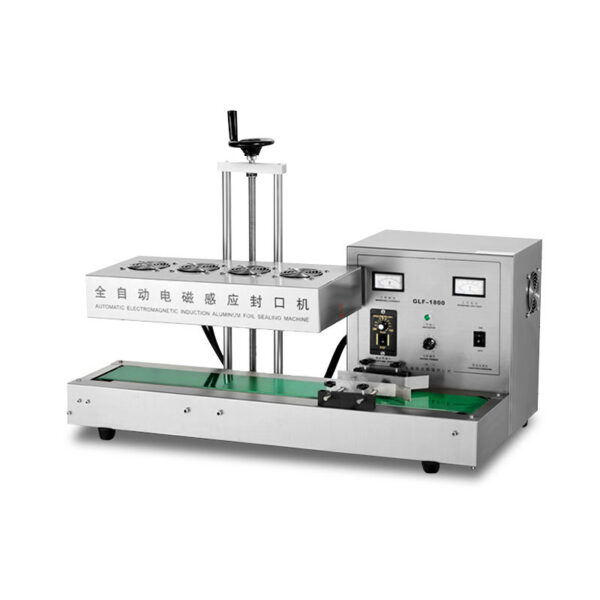

What is an Induction Sealer and How Does It Work?
An induction sealer is a device that uses electromagnetic induction to bond a foil liner to the mouth of a container, usually for tamper-evident sealing. It works by passing an alternating electromagnetic field through a metal foil liner placed on the container’s cap. This field generates heat, which melts the foil, sealing it to the container. Once the seal cools, it provides a hermetic seal that is resistant to tampering and external contaminants.
Key Features of Induction Sealing:
- Tamper-Evident Seals: The primary benefit of induction sealing is its ability to create a tamper-evident seal that ensures the product inside the container is safe and has not been altered.
- Compatibility with Various Materials: Induction sealers work with a range of materials including plastic, glass, and metal containers, making them ideal for industries like food packaging, pharmaceutical, and beverage sectors.
- Efficiency: Induction sealing is a fast process, ideal for high-volume production lines. It can seal multiple products quickly, improving operational efficiency.
Are Induction Sealers Safe?
Induction sealers are generally safe when used according to industry guidelines and standards. They have become essential in packaging operations because of their ability to create airtight, tamper-proof seals, which are crucial in food safety and product integrity. When properly maintained and operated, these machines do not pose any significant health or safety risks to workers or consumers.
Safety Features of Induction Sealers:
- No Direct Contact with Heat: Unlike heat sealing, induction sealing does not apply direct heat to the product itself. This reduces the risk of overheating or damaging sensitive products, especially in the food and pharmaceutical industries.
- Controlled Temperature: Induction sealers are designed with precise temperature control mechanisms that ensure optimal sealing without damaging the product.
- Non-Toxic Materials: The foil liners used in induction sealing are specifically designed for food and beverage safety, ensuring they do not release harmful substances into the product.
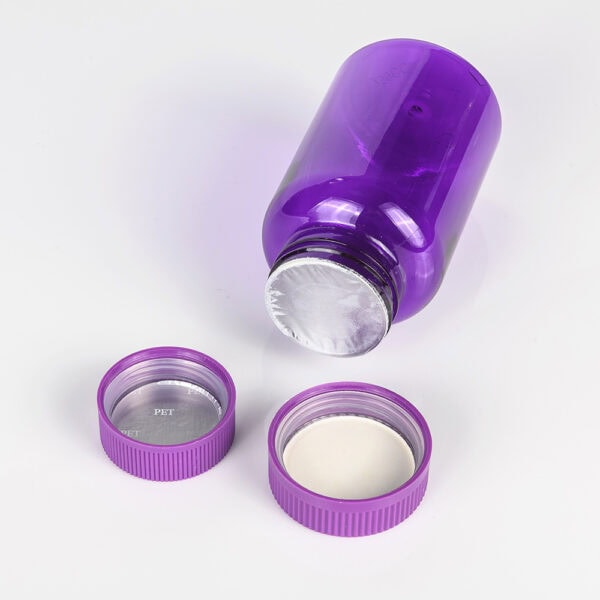

Potential Safety Risks of Induction Sealing
While induction sealing is generally safe, certain factors can introduce risks if not carefully managed:
- Improper Sealing: If the induction sealer is not calibrated correctly, the seal may be ineffective, leading to leaks or contamination.
- Electrical Hazards: Induction sealers use high-frequency electromagnetic energy, which could pose electrical hazards if the equipment is improperly maintained or used.
- Incorrect Material Use: The use of incompatible or low-quality foil liners could result in contamination or unsafe packaging.
- Heat Generation: Although the induction sealing process doesn’t apply heat directly to the product, the sealing heads themselves can become very hot. Inadequate ventilation or safety protocols could expose workers to heat-related risks.
Mitigating Risks:
- Regular Maintenance: Ensure the induction sealer is regularly inspected and maintained to ensure it operates within safe parameters.
- Proper Training: Operators should be properly trained on how to use the induction sealing equipment and handle the materials involved.
- Use Approved Materials: Always use materials approved for the specific product being packaged, including the right foil liners and packaging materials.
What Are the Disadvantages of Induction Sealing?
Though induction sealing is highly effective, it does have some disadvantages:
- Initial Cost: Induction sealing machines can be expensive to purchase and maintain, which might be a barrier for smaller businesses.
- Limited Material Compatibility: Induction sealing works best with specific container types and materials, such as plastic and glass. It may not be suitable for all types of packaging.
- Energy Consumption: Induction sealers can be energy-intensive due to the high-frequency electromagnetic fields required for operation.
- Setup Complexity: Induction sealing requires the right setup, including the correct liner material and machine calibration. This can add complexity to the packaging process.

Comparing Induction Sealing to Other Sealing Methods
Induction sealing is often compared to other methods such as heat sealing, vacuum sealing, and conduction sealing.
- Induction Sealing vs. Heat Sealing: While both methods are used to seal products, heat sealing applies direct heat to the packaging material, which can result in product degradation or damage. Induction sealing, on the other hand, does not apply direct heat, reducing the risk of overheating the product.
- Induction Sealing vs. Vacuum Sealing: Vacuum sealing is designed to remove air from the packaging to increase the product’s shelf life. Induction sealing, however, focuses on creating a tamper-evident seal and does not involve the removal of air, making it more suitable for products that require a high degree of protection against contamination.
- Induction Sealing vs. Conduction Sealing: Induction sealing involves an electromagnetic field that heats the foil liner without contact, while conduction sealing uses direct heat to bond materials together. Induction sealing tends to be faster and more efficient, especially for high-volume production.
Best Practices for Safe Induction Sealing
To ensure the safe use of induction sealers, businesses should adhere to best practices:
- Regular Calibration: Calibration ensures that the sealer applies the right amount of energy, temperature, and time to each package for a secure seal.
- Proper Operator Training: Operators should be trained on machine setup, safety protocols, and proper handling of packaging materials to minimize errors.
- Routine Maintenance: Regular maintenance and cleaning of induction sealing machines help prevent malfunctions and prolong the equipment’s lifespan.
- Quality Control: Consistent monitoring of the sealing process ensures that each product is sealed properly, preventing defective seals that could lead to contamination or product spoilage.

Conclusion
Induction sealers are a safe and highly effective method of sealing products, ensuring tamper-evidence and extending shelf life when used properly. While there are some potential risks associated with their use, these can be easily mitigated with proper machine setup, maintenance, and operator training.
For businesses looking for a reliable and secure sealing solution, investing in an induction sealer can enhance both safety and efficiency in packaging processes. Whether you’re using it for bottle labeling machines or for packaging liquids in a vacuum packaging machine, the safety and benefits of induction sealing are undeniable when applied correctly.